

In recent years, the traditional workspace has noticed a seismic shift. As per Forbes, around 12.7% of full-time employees work from home, whereas 28.2 % work in a hybrid model.
Let’s say your workplace switches to hybrid or remote, with more and more employees working from their homes where managers have limited control over what their employees are doing. In such a case, data breaches can be a severe challenge for companies to tackle.
TeamTrace’s user activity monitoring solution (UAM) deals with the root causes of data theft or security breaches. The monitoring, tracking, and overlooking of all the activities of your employees give managers better control over security, employee efficiency and issues like moonlighting and misutilization of data.
In certain cases, data breach may even stem from innocent mistakes, with no such malicious intent. However, the adverse consequence is real if anyone with unauthorized access veers into the territory of data, conducts data theft, and sells customer data, Personally Identifiable Information (PII), or corporate intellectual information for monetary gains or to cause harm deliberately.
Cybercriminals usually follow a generic pattern before attempting to breach data. They pin-point a specific organization as their target and move ahead to research victims with an attempt to locate where their vulnerabilities lie. These may include devising wicked strategies to make employees fall prey to sharing credentials or clicking potentially harmful links through phishing emails.
To understand how do data breaches occur, let’s understand what attackers set their eyes on and the strategy they follow to exploit these:
| Vulnerability Targeted | How Cybercriminals Harness it to Fulfil Their Evil Designs |
| Human Error | Phishing emails, social engineering, impersonation of IT staff or executives |
| Weak Passwords | Brute-force attacks, credential stuffing, and exploiting reused or simple passwords |
| Insider Threats | Disgruntled employees leaking data or unintentional insiders downloading malicious software |
| Third-party Vendors | Exploiting weak security measures of vendors to infiltrate supply chains |
| Unsecured Endpoints | Targeting personal devices, home networks, and unpatched software in remote work setups |
| Advanced Persistent Threats | Infiltrating networks and remaining undetected for extended periods to collect data |
| Zero-day Exploits | Using undisclosed vulnerabilities to bypass security defences before patches are developed |
| Poor Access Control | Exploiting overprivileged accounts and lack of role-based access controls to move laterally within networks |
| Cloud Misconfigurations | Accessing sensitive data through unsecured cloud storage and improperly configured services |
The most common reasons for breaches happen due to weaknesses in:
According to Bitdefender, 61% of IT security leaders have reported that their remote workers caused breaches of data privacy.
This could be a simple oversight by an individual or an infrastructural flaw within a company, both of which can be addressed with a simple solution, such as a silent tracker. This allows managers to have real-time reporting for activity tracking without disturbing and letting employees know.
Besides an unintentional or human error, cyber data security can be threatened due to:
Every data breach follows a specific lifecycle entailing five stages. Gaining a clear understanding of these phases is instrumental in curtailing the risk of data breach.
| Stage | Action Perpetrated |
| Reconnaissance | Attackers gather intelligence on the target organization, such as vulnerabilities, employee roles, or network architecture, using open-source tools or social engineering. |
| Initial Compromise | Hackers exploit vulnerabilities (e.g., phishing, malware, or misconfigured systems) to gain unauthorized access to the network or a specific system. |
| Establishing Access | Once inside, attackers install backdoors, escalate privileges, and ensure persistent access to critical systems or databases. |
| Data Exfiltration | Sensitive data is identified, collected, and transferred out of the organization, often using encryption to avoid detection. |
| Covering Tracks | In the ultimate stage of the data breach lifecycle, cybercriminals indulge in hiding all the evidence of the breach to avoid being discovered via disabling auditing features, clearing logs, or manipulating log files. |
Let’s understand the gravity of data breach effects with significant real-world examples that shook the world.
TJX Corporation is a leading multinational off-price retail company and the parent company of TJ Maxx and Marshalls. Back in 2007, the breach of TJX Corporation emerged to be the largest and costliest consumer data leak in the history of the USA.
The attackers placed traffic sniffers on the wireless networks of two stores. This allowed them to obtain information as it was dispatched from the store’s cash registers to back-end systems. Once succeeded, they infiltrated the payment processing system. That’s where the confidential cardholder data was stored.
With hackers encroaching upon 94 million customer records as data security collapsed, the company suffered huge financial losses, surpassing USD 256 million. The incident damaged TJX’s reputation, impacting customer trust and brand loyalty.
In 2013-14, Yahoo experienced two major breaches affecting all 3 billion user accounts. By exploiting a weakness in the company’s cookie system, the hackers got easy access to the names, birth dates, email addresses, phone numbers and passwords of all the users.
The complete news of the breach came to light only in 2016 while Verizon was in talks to buy the company. Due to this incident, Verizon slashed Yahoo’s purchase price by $350 million, reducing the final deal to $4.48 billion in 2017.
Data breach in Equifax, a credit reporting agency, serves as a stark reminder of the impact of poor cybersecurity practices.
In 2017, the attackers obtained the personal information of more than 143 million Americans. Apart from names and contact details, this data breach in cybersecurity laid bare crucial info, including their Social Security numbers, driver’s license numbers, and credit card numbers.
Equifax had to expend USD 1.4 billion on settlements, fines, and other costs associated with fixing the breach.
The Facebook data breach incident of 2019 involved multiple data leaks, including a massive exposure of sensitive user information. A part of this information even ended up on the dark web.
While the first dataset involved the exposition of 540 million user records, the second dataset available on the dark web leaked 267 million user records. These included the revelation of Facebook User IDs, full names, phone numbers, account names, and passwords.
The exposed data, especially phone numbers and email addresses, made users vulnerable to phishing attacks, identity theft, spamming, and social engineering attacks.
AT&T, one of the largest telecommunications companies in the United States, has experienced several significant data breaches in recent years.
Lately, in April 2024, AT&T disclosed that hackers had illegally downloaded customer data from a workspace on a third-party cloud platform. The breach affected nearly 110 million customers, making it one of the largest data breaches in the telecom sector.
The compromised data included phone numbers, call and text records, and location data. AT&T reportedly paid hackers approximately $370,000 in Bitcoin to delete the stolen phone records. Following the disclosure, AT&T’s stock experienced a 0.3% decline, equating to a $130 million loss in market capitalization.
Data breach in cybersecurity is a highly exorbitant problem. According to the Cost of a Data Breach Report by the IBM, the global average cost of a data breach is USD 4.88 million.
Owing to a surge in the popularity of remote and hybrid work mode, the cost of data breaches increased exponentially in recent years. This has necessitated organizations to implement an insider threat management software to prevent data breach.
Organizations of every size and type are subjected to the risk of data breaches. However, the severity of the incident and the costs to settle the issue may vary.
With the loss in productivity from incident response staff and other employees owing to downtime, an estimated 63,343 hours get wasted while dealing with the mishap of data breach.
Let’s have a look at the key components and statistics regarding the cost of a data breach:
| Detection & Escalation | Includes expenses for breach detection systems, forensic investigations, and crisis management. Average cost: $1.05 million. |
| Lost Business | Represents revenue loss due to customer churn, reputational damage, and operational downtime. Average cost: $1.42 million. |
| Post-breach Response | Covers legal fees, public relations, regulatory compliance, and customer notification costs. Average cost: $1.45 million. |
| Fines & Legal Penalties | Costs associated with violations of data protection laws such as GDPR or CCPA. Fines can range from millions to billions, depending on the breach severity. |
| Customer Churn | Breaches can lead to a loss of consumer trust, with affected organizations losing an average of 3%-5% of their customer base. |
| Industry Variability | Breach costs are higher in industries handling sensitive data, for instance: Healthcare: $10.93 million (highest). Finance: $5.9 million. |
| Impact of Remote Work | Organizations with remote workforces experienced an average breach cost increase of $1 million. |
To understand what other types of data breaches you should be aware of and know ways to prevent cybercrime, here is a list for you:
Phishing Attacks
This includes cybercriminals sending a deceptive message through email for trying to get personal information or clicking malicious links. These attacks often mimic the company to appear as legitimate for the individuals.
Malware Attacks
These are malicious software, including damaging, disrupting, and gaining unauthorized access to data through viruses, worms, spyware, and trojans-like attacks.
Insider Threats
76% of organizations have reported an increase in their user insider threat activity within the past five-year timespan.
This is another data breach example where the business is required to safeguard their company’s data and devices to prevent data theft.
This can be intentional harm or accident behavior from current employees to previous ones who still have access and credentials.
To prevent these data breaches, the company is required to install trustworthy anti-malware and protection to keep the data protected from attacks.
As to tackling insider threats, data leaks, and more, having an employee database, location tracker, screen monitoring, and recording-like options helps in tracking what your employees are up to.
Stolen data finds its way to the ‘Dark Web’ where it is often sold to other cybercriminals. As can be gauged from its name, the ‘Dark Web’ is that clandestine part of the Internet most people never see or access. It is not indexed by the search engines and a special kind of browser is needed to enter it.
Apart from selling personal data on the ‘Dark Web,’ cybercriminals often engage in selling illegal drugs, pornography, and various other kinds of illicit stuff. Hackers also tend to exploit sensitive data like Social Security numbers or IDs to commit fraud, such as opening bank accounts, applying for loans, or filing false tax returns.
Login details are used to access other accounts, exploiting the tendency of users to reuse passwords across platforms. Attackers utilize the obtained contact details to create highly targeted phishing scams, aiming to steal more information or money.
Conducting corporate espionage is also quite rampant. Business-critical data may be sold to competitors or used for insider trading and sabotage.
Cybercriminals can also use sensitive information to extort organizations or individuals through ransomware or blackmail. They can even manipulate data to disrupt business operations, spread misinformation, or damage reputations.
Data theft under the IT Act of Section 66 is a computer-related offense. It penalizes anyone who is in charge of the data or system for risking the company’s security.
Companies are required to report breaches and cyber attacks to CERT-In ( Indian Computer Emergency Response Team) within a six-hour deadline.
A cyber breach can threaten the company’s valuable data, leading to risking a credit rating downgrade. It can impact the ability and cost of securing finance as companies with weaker protection might have higher borrowing costs and financial risks.
As for the long-term impact, the company might suffer from losing its competitive advantage.
TeamTrace is loaded with features to protect your data from danger, including:
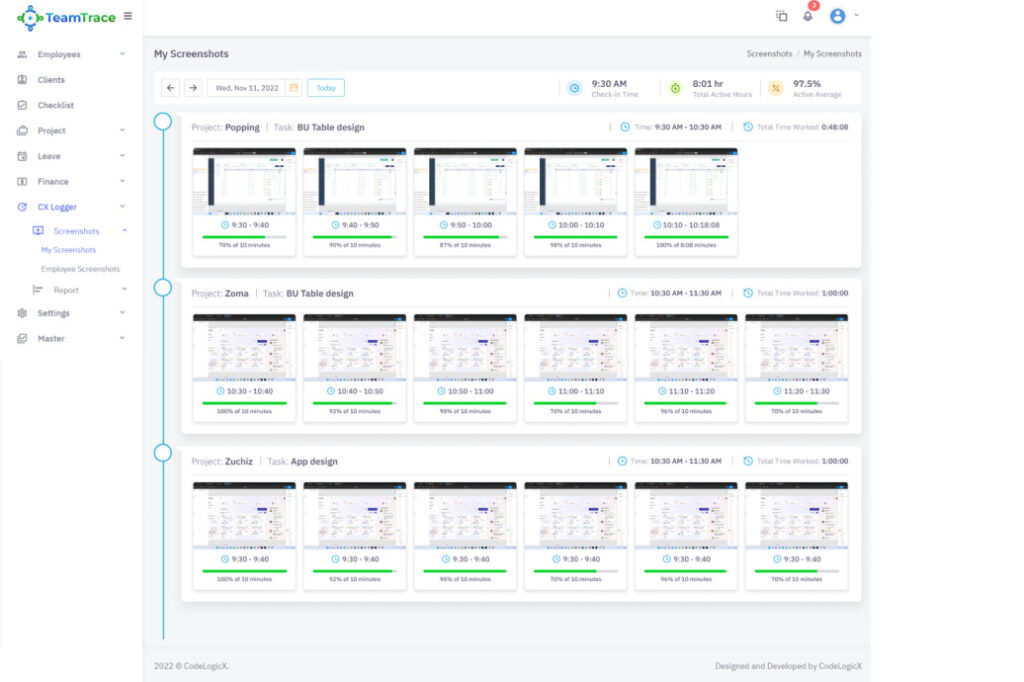
TeamTrace’s time-stamped screenshots help gain instant context and evidence against a data breach. The screenshots allow the capturing and recording of the employee’s activities and hold accountability in case of any security lapses.
Real-time screen monitoring & viewing to ensure there is no data leak from the employee’s side. It helps tackle insider threats by having a tracking report on what your employees are looking at and accessing.
Assign permission based on the department’s or individual’s specific needs to reduce the chances of unauthorized access from any third party. This ensures that data is kept safe while limiting who can access the specific information while strengthening overall data protection.
Advanced tools detect and prevent suspicious activities with the help of URL and website blockers. This allows for identity verification, access, and blocking of malicious activity. By this, the potential damage can be minimized before it becomes known as a serious data breach.
Worried about what your employees might be doing in the background? Well, install the stealth mode tracking that monitors, tracks, and records the insights on where the employees are busy without disrupting the daily workflows.
TeamTrace’s application tracking allows restricting access to the data from transferring to external devices, including USBs. This reduces the chances of data thefts or leaks, handling sensitive or confidential details without causing any risks.
With this information, the organization and managers can build their short and long-term security bridge hacking plans.
Have questions or need assistance? Our team is ready to support you with expert guidance and solutions tailored to your needs.
Talk to Us
What is Employee Burnout? Employee burnout is much more than just feeling stressed at work. It is a state of…

Project Failure Analysis: Understanding the Common Pitfalls Lack of clear vision of project goals and objectives Most projects fail because…

nice blog